The symmetrical triangle pattern is a standard chart formation used in technical analysis to predict potential breakouts in stock prices. It appears when the price of a stock is consolidating, creating a series of lower highs and higher lows that converge towards a point. This pattern indicates a period of market indecision, usually followed by a breakout in either direction. This blog delves into the symmetrical triangle pattern’s meaning, formation, and trading strategies, helping investors make informed trading decisions.
What is a Symmetrical Triangle Pattern?
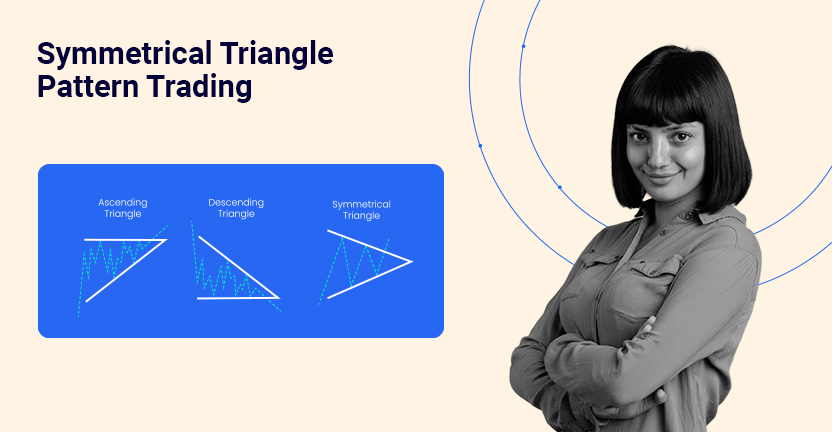
A symmetrical triangle pattern is a continuation chart pattern that forms when the price of a stock consolidates between two converging trendlines. These trendlines slope towards each other, representing a series of lower highs and higher lows. The pattern reflects a balance between buyers and sellers, leading to reduced price volatility.
The symmetrical triangle pattern is considered neutral, as the breakout can occur in either direction. Traders closely watch for a breakout above the upper trendline as a bullish signal or a breakdown below the lower trendline as a bearish signal. This pattern is commonly observed in stocks, commodities, and other financial instruments, making it a versatile tool in technical analysis.
How is the Symmetrical Triangle Pattern Formed?
The symmetrical triangle pattern is formed by connecting at least two lower highs and two higher lows using trendlines. As the price oscillates within these converging lines, it creates a triangle-like shape. Key characteristics of this pattern include:
- Converging Trendlines: The upper trendline connects the lower highs, while the lower trendline connects the higher lows. These lines slope towards each other, forming a symmetrical triangle.
- Decreasing Volume: Trading volume typically decreases as the pattern progresses, indicating market indecision and reduced activity.
- Breakout Point: The breakout usually occurs before the apex (the point where the trendlines converge). This breakout can be upward or downward, depending on the prevailing market trend.
The pattern is complete once the price breaks out of the triangle, accompanied by increased trading volume, confirming the breakout direction.
How to Identify a Symmetrical Triangle Pattern on a Chart?
To identify a symmetrical triangle pattern on a stock chart, follow these steps:
1. Identify the Trend: Confirm the existing trend before the pattern’s formation, as symmetrical triangles are typically continuation patterns.
2. Draw Trendlines: Connect at least two lower highs and two higher lows using trendlines. Ensure the lines converge, forming a symmetrical triangle.
3. Check Volume: Verify decreasing volume as the pattern progresses, indicating reduced market activity and indecision.
4. Watch for Breakout: Monitor the price movement near the apex for a breakout. A breakout above the upper trendline suggests a bullish move, while a breakdown below the lower trendline signals a bearish move.
The breakout direction often follows the prevailing trend, but waiting for confirmation with increased volume is essential.
How to Trade Using the Symmetrical Triangle Pattern?
Trading the symmetrical triangle pattern involves identifying the breakout point and confirming the breakout direction. Here’s how to trade effectively:
- Entry Point: Enter the trade when the price breaks out of the triangle with high volume. For a bullish breakout, buy when the price closes above the upper trendline. For a bearish breakout, sell or short-sell when the price closes below the lower trendline.
- Stop Loss: To minimise risk, place a stop-loss order just below the lower trendline for a bullish breakout or above the upper trendline for a bearish breakout.
- Price Target: Measure the triangle’s height at its widest point and project this distance from the breakout point. This projection helps estimate the potential price movement.
The symmetrical triangle pattern is widely used in trading stocks, commodities, and forex markets due to its reliability in predicting breakouts.
What are the Limitations of the Symmetrical Triangle Pattern?
Although the symmetrical triangle pattern is a reliable continuation pattern, it has certain limitations:
- Breakout Direction Uncertainty: The breakout can occur in either direction, making it difficult to predict the exact movement.
- False Breakouts: Price movements may break the trendline temporarily before reversing, leading to false signals.
- Volume Confirmation Needed: A breakout without increased volume may indicate a lack of momentum, increasing the risk of a false breakout.
Traders should use additional technical indicators, such as moving averages or RSI, to confirm breakouts and minimise risks.
Trading Smarter with the Symmetrical Triangle Pattern
The symmetrical triangle pattern is a powerful tool in technical analysis, helping traders identify potential breakout opportunities in stocks and other financial markets. By understanding its formation, characteristics, and breakout behaviour, investors can enhance their trading strategies and make informed decisions. Streetgains offers data-driven research and insights that help investors recognise chart patterns and navigate market trends more effectively.
Disclaimer:
The content in this blog is intended for informational purposes only and does not constitute investment advice, stock recommendations, or trade calls by Streetgains. The securities and examples mentioned are purely for illustration and are not recommendatory.
Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks. Please read all related documents carefully before investing.
Symmetrical Triangle Pattern: Meaning, Formation & Trading FAQs:
A symmetrical triangle pattern is formed when the price of a stock makes lower highs and higher lows, creating two converging trendlines. These trendlines slope towards each other, forming a triangular shape. The pattern shows a period of consolidation, reflecting market indecision before a breakout in either direction.
A symmetrical triangle indicates market indecision and a balance between buyers and sellers. It typically suggests a continuation of the previous trend but can also signal a reversal. The breakout direction, either above the upper trendline or below the lower trendline, determines the next trend.
Traders can identify breakout points by closely monitoring price movements near the triangle’s apex, where the trendlines converge. A breakout is confirmed when the price closes above the upper trendline for a bullish move or below the lower trendline for a bearish move, supported by increased trading volume.
Symmetrical triangles have converging trendlines with no apparent bias, indicating neutral market sentiment. Ascending triangles have a flat upper trendline and a rising lower trendline, suggesting a bullish breakout. Descending triangles have a flat lower trendline and a declining upper trendline, indicating a bearish breakout.
A valid breakout is confirmed when the price breaks through a trendline with a surge in trading volume. The increased volume shows strong buying or selling interest, validating the breakout direction. Additionally, a decisive price movement with minimal pullback strengthens the breakout signal.
Traders can use breakout trading strategies by entering a position once the price breaks out of the triangle with high volume. Stop-loss orders are typically placed outside the opposite trendline to manage risk. Price targets are estimated by measuring the triangle’s height and projecting it from the breakout point.
The main risks include false breakouts, where the price temporarily moves outside the trendline before reversing. The breakout direction is also uncertain until confirmation, leading to potential losses. Traders should use volume confirmation and stop-loss orders to mitigate these risks.
Streetgains provides data-driven research and technical analysis to help traders identify and validate symmetrical triangle patterns. With actionable insights and market trend analysis, traders can make informed decisions and optimise their trading strategies.
FAQs:
-
1. How to earn money daily from trading?
Earning money daily from trading involves strategies like day trading, where traders capitalise on small price movements within the same day. Success requires real-time market analysis, quick decision-making, and risk management.
-
2. How to earn money from equity trading?
To earn money from equity trading, you need to buy stocks at a lower price and sell them at a higher price. Success depends on researching companies, analysing stock trends, and using technical or fundamental analysis.
-
3. How to earn money from share trading in India?
In India, share trading offers profit potential through buying and selling stocks on exchanges like the NSE and BSE. To maximise returns, traders should use market research, tools like technical analysis, and risk management strategies.
-
4. How to make money from share trading in India?
Making money from share trading involves selecting the right stocks, timing the market, and implementing trading strategies like swing trading or day trading while staying informed about market trends.
-
5. How to transfer money from a trading account to a bank account?
To transfer money from your trading account to your bank, log into your trading platform, navigate to the funds section, and initiate a withdrawal request. The money will typically be credited to your linked bank account in 1 to 3 days.
-
6. How to withdraw money from a trading account?
You can withdraw funds by logging into your trading account, selecting the withdrawal option, and selecting the amount to transfer to your bank account. Ensure your bank account is linked and follow any steps your broker requires.
Subscribe to our Credits-Based Research System:
Pay only for successful research calls!