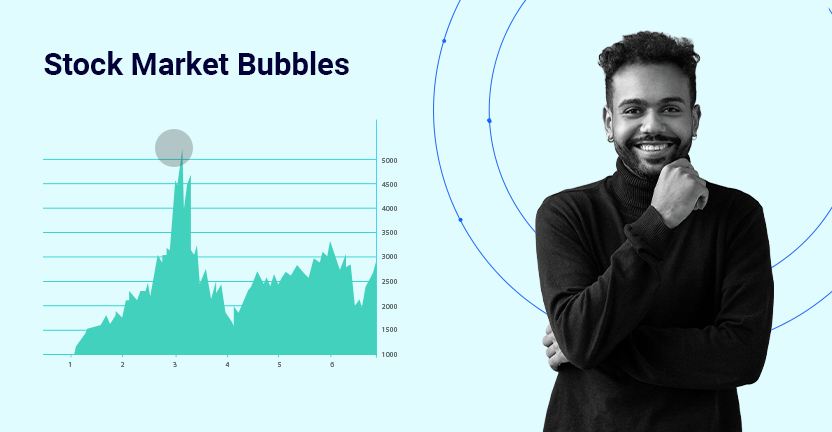
IThe stock market is often characterised by cycles of growth and correction, but sometimes, prices rise far beyond the intrinsic value of assets. This phenomenon, known as a stock market bubble, can have far-reaching consequences for economies and investors. Bubbles are typically driven by speculation, investor psychology, and external economic factors, and their eventual burst can lead to sharp corrections and losses.
In this blog, we will explore what a stock market bubble is, its causes, early warning signs, the implications of a bubble burst, and how investors can navigate such periods, especially in the context of the Indian stock market.
What Is a Stock Market Bubble?
A stock market bubble occurs when the price of stocks or other financial assets increases rapidly and irrationally, far exceeding their intrinsic value. This inflation is typically driven by excessive investor optimism and speculative behaviour, leading to unsustainable price levels.
The bubble eventually “bursts” when market confidence collapses, triggering a sharp and often widespread decline in asset prices. This can result in significant losses for investors and broader economic instability. Examples of global stock market bubbles include the Dot-Com Bubble of the late 1990s and the 2008 Financial Crisis.
What Causes a Stock Market Bubble?
Several factors contribute to the formation of a stock market bubble:
- Excessive Speculation: Investors buy assets with the sole expectation of selling them at a higher price, often ignoring fundamental value.
- Irrational Exuberance: Widespread optimism and euphoria among investors drive demand and inflate prices further.
- Low Interest Rates: Easy access to credit encourages borrowing and investment, zfuelling speculative activity.
- Market Manipulation: Sometimes, coordinated efforts by groups of traders or firms artificially inflate prices.
- Technological Innovations: New industries or technologies (e.g., dot-com companies) often attract speculative interest.
These factors create an environment where prices rise unsustainably, setting the stage for a bubble burst.
What are the Signs to identify a Stock Market Bubble?
Identifying a stock market bubble early can help investors mitigate risks. Common warning signs include:
- Rapid Price Increases: Asset prices rise steeply over a short period without corresponding fundamental improvements.
- High Valuation Ratios: Metrics like the price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio become significantly higher than historical averages.
- Excessive Media Attention: Frequent coverage and hype around specific stocks or sectors may signal speculative activity.
- Investor Overconfidence: Widespread belief that prices will continue rising indefinitely despite warning signs.
- Surge in Retail Participation: A sudden influx of inexperienced retail investors often signals the late stages of a bubble.
In the context of the Indian stock market, specific sectors or stocks periodically attract speculative interest, leading to inflated prices.
What Happens When a Stock Market Bubble Bursts?
The bursting of a stock market bubble leads to:
- Sharp Price Corrections: Asset prices plummet as investors rush to sell their holdings.
- Loss of Wealth: Both retail and institutional investors suffer significant financial losses.
- Economic Slowdowns: A burst bubble often reduces consumer spending and business activity.
- Reduced Liquidity: Credit markets tighten, making it harder for businesses and individuals to access funds.
For example, during the 2008 Financial Crisis, the bursting of the U.S. housing bubble triggered a global recession. Similarly, localised bubbles in the Indian stock market have led to sectoral corrections, impacting investors and businesses.
How Can Investors Navigate a Stock Market Bubble?
To mitigate risks during a stock market bubble, investors should adopt the following strategies:
- Focus on Fundamentals: Avoid speculative investments and prioritise stocks with strong financial health and intrinsic value.
- Diversify Portfolios: Spread investments across sectors and asset classes to reduce exposure to bubble-prone areas.
- Monitor Valuations: Monitor valuation metrics like P/E ratios and compare them to historical averages.
- Stay Informed: Track economic indicators, market sentiment, and expert analysis to identify potential bubbles early.
- Prepare for Volatility: Maintain adequate liquidity and avoid over-leveraging during speculative periods.
By staying disciplined and research-focused, investors can minimise losses and identify opportunities even during market turbulence.
The Indian Stock Market and Bubbles
The Indian stock market has witnessed its share of bubbles, often driven by speculation in specific sectors like technology, infrastructure, or small-cap stocks. Notable instances include:
- The IT Bubble (1999-2000): Fueled by excitement around the dot-com era, IT stock prices surged dramatically before collapsing.
- The Infrastructure Boom (2007-2008): Over-optimism about infrastructure projects led to inflated valuations, which corrected sharply during the global financial crisis.
Understanding these historical patterns can help investors navigate future bubbles in the Indian stock market.
Conclusion: Managing Stock Market Bubble
A stock market bubble is marked by unsustainable price increases driven by speculation and optimism, often leading to significant corrections when it bursts. While bubbles can pose risks, disciplined investing focused on fundamentals and diversification can help mitigate their impact.Streetgains, a SEBI-registered research analyst firm, offers actionable insights to guide investors through market phases, ensuring informed and sustainable investment decisions.
Disclaimer:
The content in this blog is intended for informational purposes only and does not constitute investment advice, stock recommendations, or trade calls by Streetgains. The securities and examples mentioned are purely for illustration and are not recommendatory.
Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks. Please read all related documents carefully before investing.
What Is a Stock Market Bubble? Causes, Signs, and How to Navigate It FAQs:
Bubbles form when excessive speculation, low interest rates, and market euphoria inflate asset prices. As demand increases irrationally, prices rise above their fundamental value, setting the stage for a collapse.
Signs include rapid price increases, high valuation ratios like price-to-earnings (P/E), excessive media hype, investor overconfidence, and a surge in participation by inexperienced retail investors.
Investors can track valuation metrics such as P/E and price-to-book (P/B) ratios, comparing them to historical averages. They should also watch for disconnects between asset prices and company fundamentals.
Global examples include the Dot-Com Bubble (1999-2000) and the 2008 Financial Crisis. The IT Bubble (1999-2000) and the Infrastructure Boom (2007-2008) resulted in sharp corrections in India.
Investor behaviour, such as herd mentality and irrational exuberance, often amplifies bubbles. Overconfidence and fear of missing out (FOMO) drive speculative buying, inflating asset prices further.
Speculation involves buying assets based on expected price increases rather than intrinsic value. Excessive speculation is a major driver of bubbles, creating unsustainable demand for overpriced assets.
Bubbles burst when market confidence collapses, often triggered by negative news or economic shifts. This leads to a sharp sell-off as investors rush to exit, causing asset prices to plummet.
A burst bubble results in sharp price corrections, significant wealth loss, reduced liquidity, and economic slowdowns. Investors and businesses often face long-term repercussions.
Streetgains, a SEBI-registered research analyst firm, provides well-researched insights and data-driven strategies to help investors navigate bubbles effectively. Streetgains ensures investors make informed and sustainable decisions by focusing on fundamentals and diversification.
FAQs:
-
1. How to earn money daily from trading?
Earning money daily from trading involves strategies like day trading, where traders capitalise on small price movements within the same day. Success requires real-time market analysis, quick decision-making, and risk management.
-
2. How to earn money from equity trading?
To earn money from equity trading, you need to buy stocks at a lower price and sell them at a higher price. Success depends on researching companies, analysing stock trends, and using technical or fundamental analysis.
-
3. How to earn money from share trading in India?
In India, share trading offers profit potential through buying and selling stocks on exchanges like the NSE and BSE. To maximise returns, traders should use market research, tools like technical analysis, and risk management strategies.
-
4. How to make money from share trading in India?
Making money from share trading involves selecting the right stocks, timing the market, and implementing trading strategies like swing trading or day trading while staying informed about market trends.
-
5. How to transfer money from a trading account to a bank account?
To transfer money from your trading account to your bank, log into your trading platform, navigate to the funds section, and initiate a withdrawal request. The money will typically be credited to your linked bank account in 1 to 3 days.
-
6. How to withdraw money from a trading account?
You can withdraw funds by logging into your trading account, selecting the withdrawal option, and selecting the amount to transfer to your bank account. Ensure your bank account is linked and follow any steps your broker requires.
Subscribe to our Credits-Based Research System:
Pay only for successful research calls!